Research News
-

Addressing antibiotic resistance: breath analysis aims to reduce unnecessary prescriptions
The overuse of antibiotics gives harmful bacteria the opportunity to evolve into drug resistant strains that threaten health care. To help tackle the problem, scientists in China have begun a pilot study examining biomarkers exhaled by patients.
-

New analysis provides “proof of concept” for real-time extreme event attribution
A new analysis establishes that seasonal forecast sea surface temperature (SSTs) can be used to perform probabilistic extreme-event attribution, thereby accelerating the time it takes climate scientists to understand and quantify the role of global warming in certain classes of extreme weather events.
-

Prodding leukemia cells with nanoprobes could provide cancer clues
Miniature mechanical testers have the potential to chart cell degradation in the body.
-

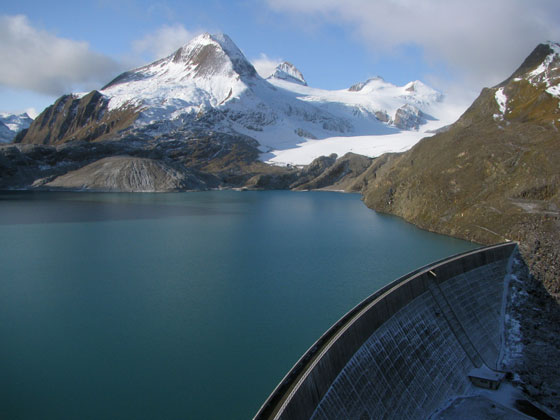
As European glaciers dwindle, could dams replace them?
Water management in reservoirs could substantially mitigate future summer water shortages, expected as a consequence of ongoing glacier retreat.
-

Poorer countries experiencing more heat extremes
Many of the world's poorest people are already experiencing more extremely hot days due to climate change, with the world’s wealthiest less affected, according to just-published Victoria University of Wellington research.
-

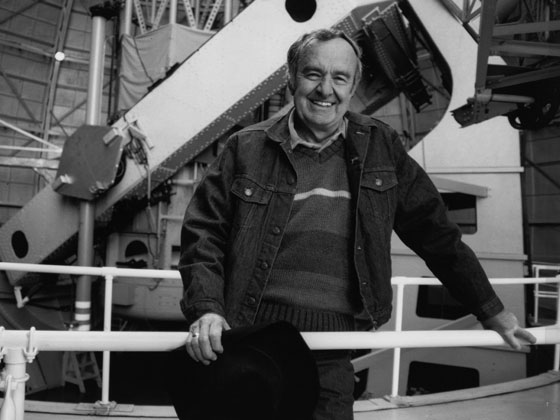
Allan Sandage’s last paper unravels 100-year-old astronomical mystery
Carnegie’s Allan Sandage, who died in 2012, was a tremendously influential figure in the field of astronomy. His final paper, published posthumously, focuses on unraveling a surprising historical mystery related to one of his own seminal discoveries.
-

Frequency of extreme heat waves on the increase in Africa: could occur annually by 2040
Climate analysis shows that periods of unusually hot weather are on the rise for one of the most vulnerable continents to climate change, even if the increase in global average temperature remains at a modest level.
-

The physics of the walking dead: the scientists studying the spread of zombies
Science writer Stephen Ornes talks with the physicists who mixed modelling with science fiction to predict the success of a zombie invasion, available in May’s issue of Physics World magazine, online now!